Vuex学习
Vuex学习
1、Vuex是什么?
1.介绍
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
2.说明:
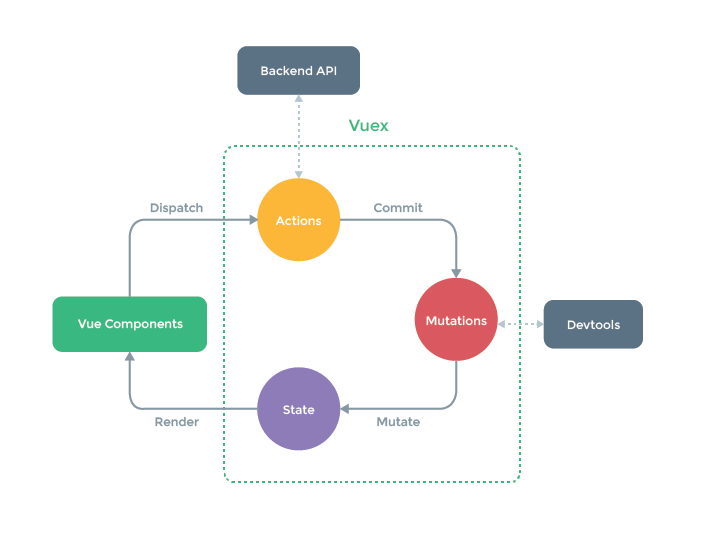
Vuex是vue组件之间数据传递的方式,任意组件都可以使用-类似大仓库
一般来说某个组件要用数据,可以调用Render读取Vuex中的数据,然后使用Dispatch调用Actions修改页面的数据,当然还有许多其他步骤,这只是最经典的动作(先读再操作)。Actions操作后会利用中间转接人Mutations去修改State,
2、安装Vuex
安装:
cnpm install vuex --save目前默认安装的是Vue3的vuex4版本,vue2需要安装指定版本,我使用的npm i vuex@3.6.2main.js 全局引入
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)
3.创建store仓库
每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)
Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同:
1. Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的,当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
2. 你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation
最简单的 Store
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
// 1.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 2.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 3.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 4.共享的数据
state:{
user:'admin',
}
})
new Vue({
router,
// 5.仓库放到(挂载)Vue实例上去
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
3、Vuex核心概念
State
1.介绍:
1. Vuex 使用单一状态树——是的,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。
2.说明:state就是存储数据仓库 容器
2.获取state数据
1、this 直接获取
this.$store.state.xxx
假如某个组件想获取刚才定义在Vuex中store仓库里state中的user数据,就可以通过this下的$store来找到
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<p>vuex-直接获取state数据:{{$store.state.user}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
created(){
console.log(this);
console.log(this.$store.state.user); //'admin'
}
}
</script>
2、mapState 辅助函数获取
了解三个使用方式:
三个辅助函数使用方法,不必掌握因为比较麻烦且不能复用计算属性
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<p>vuex-直接获取state数据:{{$store.state.user}}</p>
<p>mapState辅助函数 箭头函数 写法获取state数据:{{ user1 }}</p>
<p>mapState辅助函数 字符串 写法获取state数据:{{ user2 }}</p>
<p>mapState辅助函数 普通函数方法 写法获取state数据:{{ user3 }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1.导入辅助函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Home',
data(){
return {
msg:'你好',
}
},
// 2.使用计算属性获取state方法---了解
computed:mapState({
// 方式1、箭头函数写法(代码更简练)
user1:state=>state.user,
// 方式2、传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
user2:'user',
// 方式3、为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
user3(state) {
return state.user+'----'+this.msg;
}
}),
}
</script>需要掌握的使用方式:
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<p>vuex-直接获取state数据:{{$store.state.user}}</p>
// 4.直接使用
<p>mapState辅助函数 字符串数组写法 获取state数据:{{ user }}--{{ count }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1.导入辅助函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Home',
data(){
return {
msg:'你好',
}
},
// 2.使用计算属性获取state方法---掌握
computed:{
//3.mapState 传一个字符串数组方法 ——名称要和vuex仓库里的数据名一致 因为是数据所以放在计算属性里 注意别和data里数据名重复
...mapState(['user','count',]),
},
}
</script>当然直接把vuex放到main.js中不合适,可以单独在项目根下创建一个叫做store文件夹,里面创建一个index.js的文件
// 1. 引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 3.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 5.共享的数据
state:{
user:'admin',
count:100,
}
})
// 6.导出
export default store最后再在main.js中导入引入store
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
//路由挂载到vue实例
router,
// 仓库放到(挂载到)Vue实例
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')Mutations
1.介绍
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation
Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数
2.语法
4-2 处定义一个mutations对象,里面包含想修改state数据的方法
mutations里的方法有两个参数,比如 addCount(state,payload) –其中state是固定的state数据,payload是要携带的参数可以省略(参数可以是对象、字符串、数字)
无参数版
// 1. 引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 3.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 4-1.共享的数据 说明:state状态 任意类型
state:{
user:'admin',
count:100,
},
// 4-2.修改state仓库数据 里面包含的是方法-修改state数据
mutations:{
addCount(state){
state.count ++
},
reduceCount(state) {
state.count -= 10
}
},
})
// 5.导出
export default store有参数版
mutations:{
addCount(state,num){ //增加了一个参数需要在使用的组件里添加具体参数
state.count += num
},
reduceCount(state,{num}) {
state.count -= num
}
},
})
--------------------------------------以下是其他组件需要使用muaations时携带参数的方法-----------------------------------------------
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<h3>mutations修改state数据</h3>
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
methods:{
add(){
// 使用commit()方法调用mutations里的方法去修改state数据 同时将参数10代入
this.$store.commit('addCount',10) //即当前每次点击增加10
},
reduce(){
this.$store.commit('reduceCount',{
num:8
})
}
},
}
</script>3.操作方法:
1、直接操作mutations
直接使用commit()方法调用mutations里的方法去修改state数据
在需要修改的组件里使用 this.$store.commit(state,payload) –state是定义在mutations里的方法名,payload是参数需要看mutations里的方法是否可以省略
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<h3>mutations修改state数据</h3>
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
methods:{
add(){
// 注意:不能直接修改 仓库不会同步视图
// this.$store.state.count = 200
// 使用commit()方法调用mutations里的方法去修改state数据
this.$store.commit('addCount',)
},
reduce(){
this.$store.commit('reduceCount',)
}
},
}
</script>2、辅助函数操作
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<h3>mutations修改state数据</h3>
<button @click="add2">辅助函数+</button>
<button @click="reduce2">辅助函数-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1.引入辅助函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Home',
methods:{
// 2.mapMutations 是方法所以放在methods里
...mapMutations(['addCount','reduceCount']),
add2(){
// 3.操作辅助函数
this.addCount(20)
},
reduce2(){
this.reduceCount({
num:20
})
}
},
}
</script>3、Mutation 必须是同步函数
一条重要的原则就是要记住 mutation 必须是同步函数
4、 Mutation 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
Vuex 中的 mutation 也需要与使用 Vue 一样遵守一些注意事项:
1. 最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
1. 当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该
使用 Vue.set(obj, ‘newProp’, 123), 或者
以新对象替换老对象。例如,利用对象展开运算符 (opens new window)我们可以这样写:
state.obj = { …state.obj, newProp: 123 }
mutations:{
addCount(state,num){
state.count += num
},
reduceCount(state,{num}) {
state.count -= num
},
// 修改已经存在的属性
changeUserinfo(state,payload){
state.userinfo.uname = payload.uname
},
// 添加数据
addUserinfo(state,payload){
// 直接增加属性 数据会修改 但是视图不同步
// state.userinfo.love = payload.love;
// 解决方式:
// 1.提前定义好属性
// 2.Vue.set(obj,'属性','值')
// 3.{...}
// 4.Object.assign()
Vue.set(state.userinfo,'love',payload.love)
}
},组件中使用: 当添加一个没有存在的属性 state会添加成功但是页面不会显示,因为对象里的属性地址是没有改变的vue检测不到
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>我是about</h2>
<p>获取userinfo数据:{{userinfo}}</p>
<button @click="addobj">对象添加一个不存在的属性</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex"
export default ({
computed:{
...mapState(['userinfo'])
},
methods:{
change(){
// 直接修改state数据
this.$store.commit('changeUserinfo',{
uname:'zimo'
})
},
// 当添加一个没有存在的属性 state会添加成功但是页面不会显示,因为对象里的属性地址是没有改变的vue检测不到
addobj(){
this.$store.commit('addUserinfo',{
love:'擦擦擦'
})
}
}
})
</script>5、 使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
使用常量替代 mutation中 事件类型(即方法的名称)在各种 Flux 实现中是很常见的模式。这样可以使 linter 之类的工具发挥作用,同时把这些常量放在单独的文件中可以让你的代码合作者对整个 app 包含的 mutation 一目了然:
首先在store下新建js文件,里边写一个对象暴露出去
/*
* 定义mutations事件类型:函数名称
定义常量
*/
export const ADDCOUNT = 'ADDCOUNT';在需要用到mutations的组件里这样使用
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>我是home</h2>
<h3>mutations修改state数据</h3>
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button @click="reduce">-</button>
<button @click="add2">辅助函数+</button>
<button @click="reduce2">辅助函数-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 辅助函数
import { mapState,mapMutations } from 'vuex'
//1. 导入常量js
import { ADDCOUNT, } from '../store/mutation-types.js'
export default {
name: 'Home',
computed:{
...mapState(['user','count',]),
},
methods:{
// 2.辅助函数里也改成定义的常量名
...mapMutations([ADDCOUNT,'reduceCount']),
add(){
// 3.使用commit()方法调用mutations里的方法也要改为常量名
this.$store.commit(ADDCOUNT,10)
},
reduce(){
this.$store.commit('reduceCount',{
num:8
})
},
add2(){
//4. 其他直接使用辅助函数+的地方也改为常量名
this.ADDCOUNT(20)
},
reduce2(){
this.reduceCount({
num:20
})
}
},
}
</script>Action
1、介绍
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
2、例子
注册一个简单的 action:
action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
increment (context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
}
})3、操作Action
1.直接获取actions
this.$store.dispatch('actions里的函数名')2.辅助函数获取actions
// 1.引入mapActions辅助函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
//2.在方法里面调用
methods: {
...mapActions(['increment']),
add() {
//3.使用辅助函数里的方法
this.increment(100)
}
}
}4、实际上手练习
1.定义actions对象
首先在vuex文件下定义actions对象(4-3),准备一个异步函数,第一个参数context与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性,第二个参数是因为mutstions里减法函数需要一个对象参数num,使用context.commit()方法,第一个参数是mutations里的方法名称,第二个参数是接收上边传递的参数
// 1. 引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 3.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 4-1.共享的数据 说明:state状态 任意类型
state:{
count:100,
},
// 4-2.修改state仓库数据 里面包含的是方法-修改state数据
mutations:{
reduceCount(state,{num}) {
state.count -= num
},
},
// 4-3. actions操作异步 执行mutations
actions:{
// 定义函数-异步
asyncReduceCount(context,payload) {
//模拟异步请求 5秒后操作上面的mutations里的减法函数 reduceCount
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('reduceCount',payload)
},2000)
}
}
})
// 5.导出
export default store2.在组件上使用
1、组件里直接调用actions
使用this.$store.dispatch('想要调用的actions里的方法名称',’需要传递的num值‘)
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>我是about</h2>
<h3>操作actions</h3>
<p>vuex-count:{{$store.state.count}}</p>
<button @click="jian">actions 直接调用</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default ({
methods:{
jian(){
this.$store.dispatch('asyncReduceCount',{
num:10
});
}
}
})
</script>2、组件里使用辅助函数方法调用actions
例子1
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>我是about</h2>
<h3>操作actions</h3>
<p>vuex-count:{{$store.state.count}}</p>
<button @click="jian2">actions 辅助函数调用</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapActions } from "vuex"
export default ({
methods:{
...mapActions(['asyncReduceCount']),
jian(){
//直接调用actions
this.$store.dispatch('asyncReduceCount',{
num:10
});
},
jian2(){
// 辅助函数方法调用actions
this.asyncReduceCount({num:20})
}
}
})
</script>例子2
组件获取state里的用户名
安装一下axios
cnpm i axios - S
然后在vuex文件下store仓库的代码如下
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//1.定义一个空的用户名
user:'',
},
mutations:{
// 2.定义一个修改state的user函数
changeUser(state,uname){
state.user = uname
},
},
actions:{
// 3.定义一个异步请求--用户名的函数
getUser(context){
axios.get('http://iwenwiki.com/api/blueberrypai/getIndexBanner.php')
.then(res => {
console.log(res.data.banner[0].title);
// 4.数据获取成功后,解析出来想要的数据格式 --再利用mutations来修改状态state
// 5.操作-mutations可以使用contxet.commit('要操作的方法名','其他参数')来修改用户名
context.commit('changeUser',res.data.banner[0].title)
})
}
}
})在组件里的代码如下
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>我是about</h2>
<p>用户名:{{user}}</p>
<button @click="getUser1">获取用户名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapActions } from "vuex"
export default ({
computed:{
...mapState(['userinfo','user'])
},
methods:{
...mapActions(['asyncReduceCount','getUser']),
getUser1(){
this.getUser()
},
}
})
</script>Getter
1、介绍
Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义“getter”(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。对数据缓存和过滤处理。
2、如何访问
1.直接获取getters
this.$store.getters.属性
2.辅助函数访问
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([ 'doneTodosCount','anotherGetter'])
}
}3、例子
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
user:'',
},
mutations:{
},
actions:{
},
getters:{
userName:state=>{
return state.user +'vip用户'
}
}
})其他组件使用
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>我是about</h2>
<h4>getters使用</h4>
<p>用户名:{{user}}</p>
<p>新的用户名直接读取:{{$store.getters.userName}}</p>
<p>新的用户名辅助函数读取:{{userName}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//1. 导入辅助函数
import { mapState,mapActions,mapGetters } from "vuex"
export default ({
// 2.计算属性中使用辅助函数
computed:{
...mapState(['userinfo','user']),
...mapGetters(['userName'])
},
})
</script>总结
1、vuex仓库数据 state getters
1.state 获取:
1、直接获取
this.$store.state.xx
2、辅助函数获取
//引入辅助函数...
import { mapState } from "vuex"
computed:{
...mapState(['','',...])
} 2.getters获取:
1、直接获取
this.$store.getters.xx
2、辅助函数获取
//引入辅助函数...
import { mapGetters } from "vuex"
computed:{
...mapGetters(['','',...])
} 2、操作修改state –mutations actions
1.mutations操作
1、直接获取
this.$store.commit(‘函数名字’,’参数’)
2、辅助函数获取
//引入辅助函数...
import { mapMutations } from "vuex"
computed:{
...mapMutations(['','',...])
} 2.actions操作
1、直接获取
this.$store.dispatch(‘函数名字’,’参数’)
2、辅助函数获取
//引入辅助函数...
import { mapActions } from "vuex"
computed:{
...mapActions(['','',...])
} Modules
1、介绍:
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块
简单来说store还有一个modules属性对象里面可以单独存储入:用户信息、城市数据、购物车数据、搜索数据等等
2、命名空间:
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。
3、modules的使用:
4-5 处写一个modules对象,添加一个模块名称的属性对象,里面可以包含state,mutations,actions,getters
// 1. 引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { ADDCOUNT } from './mutation-types.js'
// 3.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 4-1.共享的数据 说明:state状态 任意类型
state:{},
// 4-2.修改state仓库数据 里面包含的是方法-修改state数据
mutations:{},
// 4-3. actions操作异步 执行mutations
actions:{},
// 4-4. getters 处理state数据进行加工
getters:{},
// 4-5. modules 模块 分类存储很多信息
modules:{
// 1、例:存城市数据
cityModule:{
// 开启了命名空间 让actions mutations getters的作用域是当前的模块下而不是挂载到全局
namespaced:true,
state:{
cityName:'成都',
},
mutations:{
changeCity(state,payload){
state.cityName = payload
}
},
actions:{
// 也可以写成这种格式 getCity({commit},city)
getCity(context,city){
context.commit('changeCity',city)
}
}
},
}
})
// 5.导出
export default store在需要用到的模块组件下使用:
<template>
<div>
<h2>城市模块的使用</h2>
<h4>state</h4>
<p>当前城市--直接读取:{{this.$store.state.cityModule.cityName}}</p>
<p>当前城市--辅助函数读取:{{cityName}}</p>
<h4>mutations</h4>
<button @click="getCity1">修改城市城名</button>
<button @click="getCity2">辅助函数修改城市城名</button>
<h4>actions</h4>
<button @click="updateCity1">actions-修改城市城名</button>
<button @click="updateCity2">actions-辅助函数修改城市城名</button>
<h4>getters</h4>
<!-- getters这里不能直接打点调用下面的方法,而是用中括号加引号 -->
<p>getters--获取数据:cityVal:{{this.$store.getters['cityModule/cityVal']}}</p>
<p>getters--辅助函数获取数据:cityVal:{{this.cityVal}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapMutations,mapActions,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods:{
...mapMutations('cityModule',['changeCity']),
...mapActions('cityModule',['getCity']),
getCity1(){
// 1、直接获取模块下的mutations
this.$store.commit('cityModule/changeCity','南京')
},
getCity2(){
// 2、辅助函数获取模块下的mutations下的changeCity方法
this.changeCity('南京')
},
updateCity1(){
//1、直接使用actions模块下的getCity方法
this.$store.dispatch('cityModule/getCity','北京')
},
updateCity2(){
// 2、辅助函数获取模块下的actions的getCity
this.getCity('北京')
}
},
computed:{
// ...mapState('模块名称',['模块里的变量'])
...mapState('cityModule',['cityName']),
...mapGetters('cityModule',['cityVal'])
}
}
</script>4、带命名空间的模块内访问全局内容
1.在getter对象里的四个参数
如果你希望使用全局 state 和 getter,rootState 和 rootGetters 会作为第三和第四参数传入 getter,也会通过 context 对象的属性传入 action
// 4-5. modules 模块 分类存储很多信息
modules:{
// 1、例:存城市数据
cityModule:{
// 开启了命名空间 让actions mutations getters的作用域是当前的模块下而不是挂载到全局
namespaced:true,
state:{
cityName:'成都',
},
getters:{
cityVal:state=>{
return state.cityName + '好去处'
},
// getGlobalCity方法 --getter数据处理的时候,获取全局的getters state数据
getGlobalCity(state,getters,rootState,rootGetters){
// state 获取当前模块的状态-state
// getters 获取当前模块的所有的getterrs
// rootState 获取根上的state数据 可以获取其他模块的数据
// rootGetters 获取根上所有的getters 全局的和所有模块的getters
console.log(state,getters,rootState,rootGetters);
}
},
mutations:{
changeCity(state,payload){
state.cityName = payload
}
},
actions:{
// 也可以写成这种格式 getCity({commit},city)
getCity(context,city){
context.commit('changeCity',city)
},
// 注意:局部模块的context对象可以访问全局对象 state getters mutations getters 包括其他模块 !
getGlobalCityAction(context){
console.log(context);
}
}
},
}组件中使用 如下, // 同时局部模块的context对象可以访问全局对象 state getters mutations getters 包括其他模块
<template>
<div>
<h4>模块内访问全局的数据state getters</h4>
<button @click="getGetters" >访问getters</button>
<button @click="getGlobalCityAction1" >访问局部模块的context对象</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapMutations,mapActions,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods:{
...mapMutations('cityModule',['changeCity']),
...mapActions('cityModule',['getCity','getGlobalCityAction']),
getGetters(){
// console.log(this.getGlobalCity);
this.getGlobalCity
},
getGlobalCityAction1(){
this.getGlobalCityAction()
}
},
computed:{
// ...mapState('模块名称',['模块里的变量'])
...mapState('cityModule',['cityName']),
...mapGetters('cityModule',['cityVal','getGlobalCity'])
}
}
</script> 2.{ root: true } 第三参数
需要在全局命名空间内分发 (触发) action 或提交 mutation,将 { root: true } 作为第三参数传给 dispatch 或 commit 即可
actions方法接收一个context对象,使用context.commit()方法能操作mutation,第一个参数是mutations里的方法名称,第二个参数是接收上边传递的参数,所以当第三个参数是{ root: true } 的时候,将可以访问到全局下的mutation,同理dispatch下能访问到全局下的action里的xx方法解释:就是在命名的模块内想要访问全局的actions或者mutaitons里面的函数
语法:actions里面: context.commit(‘changeUser’,null,{root:true})
例如:在命名的模块下,如果对象想访问全局的actions 或者是全局的mutations 都是可以的
// modules 模块 分类存储很多信息
modules:{
mutations:{
changeCity(state,payload){
state.cityName = payload
}
},
actions:{
// 局部模块的context对象可以访问全局对象 state getters mutations getters 包括其他模块
// context对象里面包含了={dispatch:'',commit:'',state:'',getters:'',rootState:'',rootGetters:''}
getGlobalCityAction(context){
console.log(context);
// 如果对象想访问全局的actions 或者是全局的mutations 都是可以的 这里访问全局的mutations方法修改全局state数据
context.commit('changeUser','局部修改全局的user',{root:true})
}
}
},!!注意:
1、commit
actions里的方法能够使用commit去调用mutations里的方法,
actions方法接收一个context对象,使用context.commit()方法能操作mutation,第一个参数是mutation里的方法名称,第二个参数是接收上边传递的参数,2、dispatch
能够使用dispatch调用action里面的方法
项目结构
1、规则
虽然vuex设计并不限制你的代码结构,但是,它规定了一些需要遵守的规则:
a: 应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中。(所有的数据都要在 new Vuex.Store中)
b: 提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的。(想改state数据只能通过mutation的方法去修改)
c: 异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面。
只要你遵守以上规则,如何组织代码随你便。
2、项目结构实例
通过上方的学习后会发现vuex文件已经有一百多行代码,看起来较为麻烦。vuex设计了只需将 action、mutation 和 getter 分割到单独的文件。
项目结构示例
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块在store文件夹下新建state 、mutations 、actions 、getterrs 后辍为.js的文件,模块文件需要单独在store下新建modules文件夹放入各个 模块名.js,然后将原store里的代码移动过去,并暴露出来,重新将项目分割后如下:
// 1. 引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2.引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 拆分后:引入state mutations actions getterrs 和命名空间模块cityModule、loginModule
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './actions'
import getters from './getters'
import cityModule from './modules/cityModule'
import loginModule from './modules/loginModule'
// 3.使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4.创建Vuex仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 4-1.共享的数据 说明:state状态 任意类型
state:state,
// 4-2.修改state仓库数据 里面包含的是方法-修改state数据
mutations:mutations,
// 4-3. actions操作异步 执行mutations
actions:actions,
// 4-4. getters 处理state数据进行加工
getters:getters,
// 4-5. modules 模块 分类存储很多信息
modules:{
// 1、例:存城市数据
cityModule:cityModule,
// 2、例:存用户的数据
loginModule:loginModule,
}
})
// 5.导出
export default store